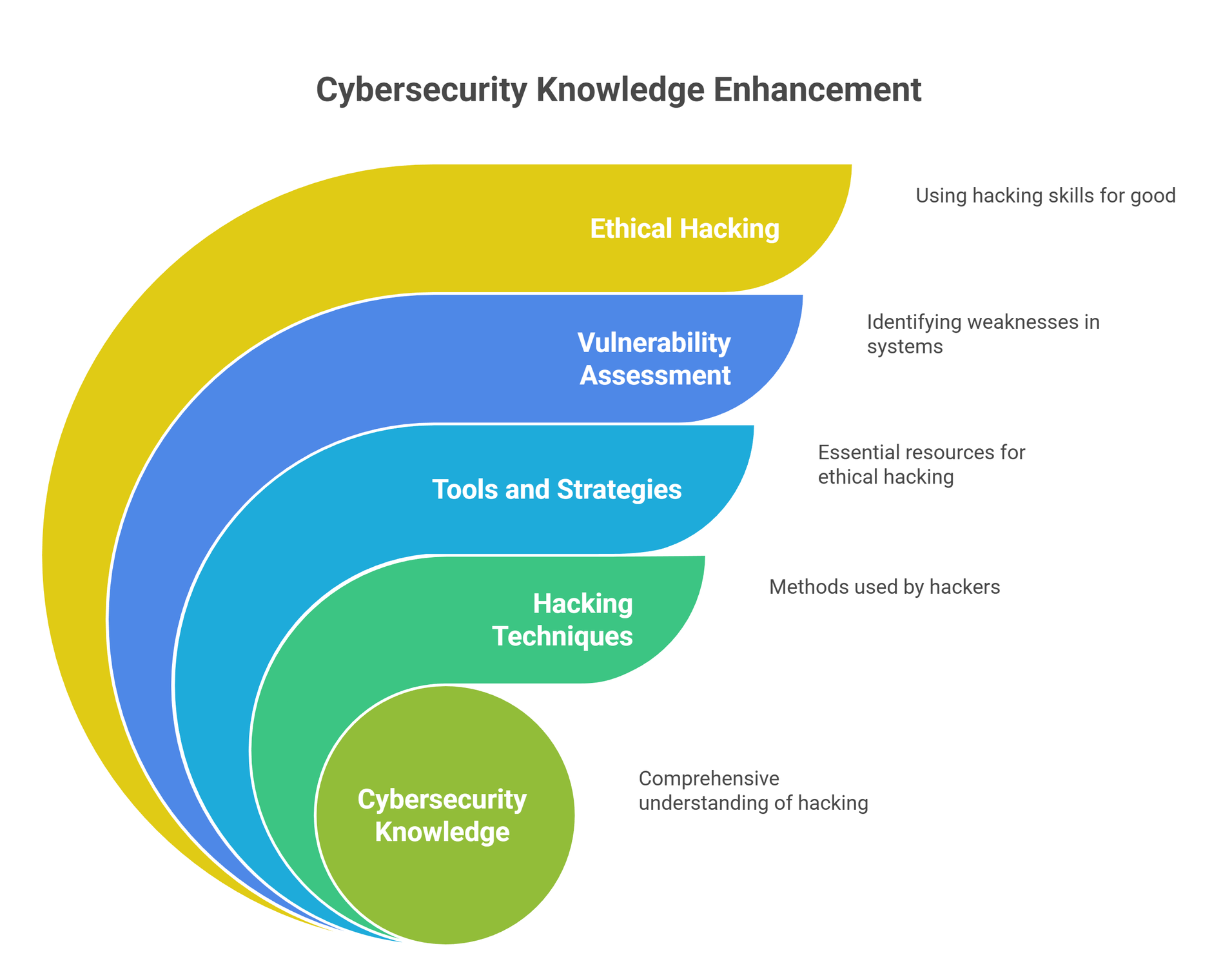
Basics of Hacking
🔐 What Is Hacking?
Hacking is the process of finding weaknesses in computer systems, networks, or websites and understanding how those weaknesses can be used to access data, control systems, or test security.
In simple words, hacking is about how things break — and how they can be secured. Today, hacking is not only used for crime, but also for cybersecurity testing, digital protection, and national security.
Millions of companies around the world legally hire hackers to test their security before real attackers do. This is where ethical hacking and cybersecurity careers are born.
🧠 How Does Hacking Actually Work?
Hacking does not start with “breaking into systems.” It starts with understanding how systems work:
How the internet sends data
How websites communicate with servers
How users log in
How software processes requests
Hackers then look for:
Misconfigurations
Weak passwords
Badly written code
Exposed services
Unprotected APIs
Once a weakness is found, hackers test how far access can go — always legally in ethical hacking.
👉 In structured learning paths and courses, these concepts are taught with safe practice labs and real-life simulations, not random experiments.
🚀 Why Learning Hacking Is a Powerful Skill Today
Hacking is no longer just a “tech hobby” — it is a high-demand professional skill. Ethical hackers work as:
Penetration Testers
Bug Bounty Hunters
SOC Analysts
Security Engineers
Cloud Security Experts
With cyberattacks increasing every year, organizations urgently need people who think like attackers to stop attackers.
If you understand what hacking really is from the basics, you unlock opportunities in:
Cybersecurity jobs
Freelance security testing
Bug bounty programs
Digital defense roles
👉 This is why most learners start with a basic hacking course or structured beginner roadmap to avoid confusion and learn safely.
Types of Hackers
Not all hackers are the same. Some work to protect systems, while others try to exploit them for personal gain. Understanding the different types of hackers is one of the most important steps in learning cybersecurity and ethical hacking. Hackers are mainly categorized based on their intent, permission, and actions. Knowing these categories helps you understand who is protecting the internet and who is attacking it.
🔹 White Hat Hackers (Ethical Hackers)
These are the good hackers. They work with permission to:
Test websites and networks
Find security weaknesses
Protect organizations from cyberattacks
White hat hackers work as penetration testers, security analysts, and bug bounty hunters.
👉 Most people who learn hacking through structured courses and legal practice labs aim to become white-hat hackers.
🔹 Black Hat Hackers (Illegal Hackers)
These are the bad actors who hack for:
Stealing data
Financial fraud
Spreading malware
Personal gain
Black hat hacking is illegal and punishable by law. Understanding how black hat attackers think helps ethical hackers defend systems better.
🔹 Gray Hat Hackers (Between Good & Bad)
Gray hat hackers fall in between white and black hats. They may:
Find vulnerabilities without permission
Not always exploit them fully
Sometimes report issues later
Even if their intent is not always harmful, acting without permission is still legally risky.
🚨 Other Important Hacker Types You Should Know
Beyond the main three, there are other important categories:
Script Kiddies – Beginners who use ready-made tools without deep knowledge
Hacktivists – Hackers driven by social or political causes
State-Sponsored Hackers – Government-backed cyber units
Cyber Terrorists – Hackers who aim to create fear and large-scale damage
Understanding these roles helps you see how real-world cyber warfare and digital threats work.
🚀 Why Understanding Hacker Types Matters in Your Learning Journey
When you understand the types of hackers, you also understand:
How attacks are planned
Why different attackers target different systems
What skills ethical hackers need to develop
How bug bounty platforms and cybersecurity jobs work
If your goal is to become an ethical hacker or bug bounty hunter, you must clearly know:
✅ What kind of hacker you want to be — and
❌ What kind of hacker you must never become.
👉 That’s why beginner-friendly ethical hacking courses always start with hacker types and real-world attacker mindsets before moving into tools and attacks.
How the Internet & Networking Works
The internet is a massive global network where billions of devices communicate with each other every second. When you open a website, send a message, or watch a video, your data doesn’t travel magically—it moves through routers, servers, cables, and wireless signals.
Your device sends a request → it travels through multiple networks → reaches the server → and comes back with a response.
This entire process happens in milliseconds, and attackers look for weaknesses inside this journey.
👉 In beginner networking courses, this flow is explained with diagrams and real examples so learners don’t feel confused.
🔗 Core Networking Basics Every Hacker Must Know
To understand hacking, you must first understand how systems talk to each other. The most important basics include:
IP Address – Identity of a device on the internet
DNS – Turns website names into IP addresses
Ports & Protocols – Determine how data enters and exits systems
HTTP & HTTPS – How websites send and receive information
TCP/IP – The backbone of internet communication
Hackers look for:
Open ports
Weak protocols
Misconfigured servers
Exposed services
👉 These concepts are taught in a step-by-step networking module inside structured hacking courses, making them easy even for non-technical beginners.
🛡️ Why Networking Knowledge Is Critical for Ethical Hacking
Without networking knowledge, hacking tools look like random commands. But with proper understanding, you can:
✅ Know what a scan result actually means
✅ Understand how firewalls work
✅ Detect suspicious traffic
✅ See how attacks move across networks
✅ Build a strong base for web hacking, bug bounty, and SOC roles
This is why professional hackers always learn networking before real-world attacking.
👉 Most successful ethical hackers start with a basic networking + hacking foundation course to avoid blind tool usage and long-term confusion.
Linux Fundamentals for Hackers
🐧 Why Hackers Prefer Linux Over Windows
Linux is the most powerful operating system for ethical hacking and cybersecurity. Almost all professional hacking tools, scanners, and frameworks are built to work best on Linux-based systems like Kali Linux, Parrot OS, and Ubuntu.
Unlike regular operating systems, Linux gives you:
Full control over the system
Deep access to networking features
Better performance for security tools
Strong customization and automation power
This is why most ethical hackers, bug bounty hunters, and SOC analysts use Linux as their primary OS.
👉 In structured beginner courses, Linux is taught from zero so anyone can start without fear.
💻 Essential Linux Commands Every Beginner Must Know
You don’t need to be a Linux expert to start hacking—but you must know the basics like:
File & folder navigation
Checking network connections
Managing permissions
Installing tools
Running security scripts
Using the terminal confidently
Without these basics, even the best hacking tools feel confusing and useless.
👉 That’s why most learners start with a Linux for Hackers module inside beginner hacking courses, where commands are taught with real hands-on practice instead of theory.
🚀 How Linux Skills Accelerate Your Hacking & Bug Bounty Journey
Once you understand Linux fundamentals, you can:
✅ Install and use tools like Nmap, Burp, Metasploit
✅ Perform scans and recon smoothly
✅ Automate tasks with scripts
✅ Analyze logs and network traffic
✅ Move confidently into web hacking, bug bounty & pentesting
Linux is not just an operating system—it’s your main weapon as a hacker.
👉 This is why every serious learner upgrades from basic Linux knowledge to a full ethical hacking foundation course that includes Linux + networking + real tools.
Understanding Vulnerabilities & Exploits
🛑 What Is a Vulnerability in Cybersecurity?
A vulnerability is a weakness or flaw in a system, website, software, or network that can be misused by attackers. These weaknesses may exist due to:
Poor coding
Weak passwords
Outdated software
Misconfigured servers
Insecure user input handling
Vulnerabilities are not guesses — they are real technical mistakes that attackers look for every day.
✅ Ethical hackers search for these flaws to fix them before criminals exploit them.
👉 In structured beginner courses, vulnerabilities are explained with simple real-world examples so learners don’t feel overwhelmed by technical terms.
💥 What Is an Exploit & How Attacks Really Happen?
An exploit is the actual method or technique used to take advantage of a vulnerability.
If a vulnerability is a door left open, an exploit is the way an attacker walks through that door.
For example:
A login weakness = vulnerability
Bypassing that login = exploit
Exploits may be used to:
Access private data
Gain system control
Upload malware
Bypass authentication
Deface websites
👉 In ethical hacking courses, exploits are demonstrated in safe lab environments only, so learners understand the process without breaking laws.
🎯 Why Vulnerabilities & Exploits Are the Core of Hacking
Every hacking technique is built on two things only:
✅ Finding vulnerabilities
✅ Using exploits responsibly (for security testing)
When you clearly understand this concept, you can:
Read vulnerability reports (CVEs)
Understand bug bounty write-ups
Analyze how real cyberattacks happen
Learn web security, cloud security, and network security faster
Move confidently into bug bounty & pentesting
👉 This is why most ethical hackers start with a foundation course that deeply explains vulnerabilities & exploits before touching advanced tools.
Intro to Web Security (OWASP Basics)
🌐 What Is Web Security & Why It Matters Today
Web security is the practice of protecting websites and web applications from cyberattacks, data theft, and unauthorized access. Since most businesses operate online, websites have become the number one target for hackers.
From login pages to payment systems, every feature of a website can contain:
Weak code
Poor authentication
Misconfigured servers
Unsafe user input handling
If these issues are not fixed, attackers can steal data, take control of accounts, or even shut down entire platforms.
👉 That’s why modern ethical hacking and bug bounty learning always includes a strong web security foundation through structured courses.
🧾 What Is OWASP & The OWASP Top 10 Explained Simply
OWASP (Open Worldwide Application Security Project) is a global organization that creates free security standards for web applications.
The OWASP Top 10 is a list of the most critical web security risks in the world.
Some common OWASP risks include:
SQL Injection
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Broken Authentication
Security Misconfigurations
Insecure APIs
These vulnerabilities are responsible for most real-world website hacks.
👉 In beginner-friendly courses, the OWASP Top 10 is taught with simple demos, visuals, and safe practice environments so learners truly understand how attacks work.
🚀 How OWASP Knowledge Boosts Bug Bounty & Hacking Skills
Once you understand OWASP basics, you can:
✅ Identify common web vulnerabilities
✅ Read bug bounty reports easily
✅ Test login panels and forms safely
✅ Understand how attackers break websites
✅ Start practicing real web security testing
This knowledge is the gateway to bug bounty hunting, web pen testing, and security research.
👉 That’s why most learners move from OWASP basics into a complete web security or bug bounty course that teaches each vulnerability step by step.
Reconnaissance & Scanning Basics
🔍 What Is Reconnaissance in Ethical Hacking?
Reconnaissance (Recon) is the very first step of hacking where an ethical hacker collects information about a target before testing its security. This information can include:
Domain & subdomains
IP addresses
Server location
Technologies used (CMS, frameworks, servers)
Open services and exposed data
Recon is about observing without attacking. A strong recon phase often decides whether a security test will be successful or fail.
👉 In beginner-friendly courses, recon is taught with legal, real-world examples and safe practice targets, so learners build confidence without risk.
📡 What Is Scanning & How It Finds Hidden Weak Points
Once recon is done, the next step is scanning. Scanning is used to actively look for open ports, running services, and possible vulnerabilities.
Scanning helps you discover:
Open ports (like 80, 443, 21, 22)
Backend services
Firewall behavior
Weak network configurations
This step turns information into actionable security data.
👉 In structured hacking courses, scanning is taught using guided tool setups and controlled environments, not random internet targets.
🚀 Why Recon & Scanning Are Crucial for Bug Bounty & Pentesting
Recon and scanning are the foundation of bug bounty hunting and penetration testing. With these skills, you can:
✅ Discover hidden attack surfaces
✅ Find real vulnerability entry points
✅ Understand how attackers map a target
✅ Save hours of random testing
✅ Increase success in bug bounty programs
Most successful hackers spend more time on recon than on actual exploitation.
👉 That’s why every serious learner upgrades from basic theory to a full practical recon & scanning module inside an ethical hacking course.
Beginner Tools & Ethical Rules
🛠️ Essential Beginner Hacking Tools You Should Know
As a beginner, you don’t need hundreds of tools — you only need the right foundational tools to understand how security testing works. Some common beginner-level tools include:
Nmap – For network and port scanning
Burp Suite – For testing web application requests
Wireshark – For analyzing network traffic
Subfinder – For discovering subdomains
Linux Terminal – For running security commands
These tools help you observe, analyze, and understand how systems behave, which is the real goal at the beginner stage.
👉 In structured ethical hacking courses, these tools are taught using safe targets and beginner-friendly walkthroughs, so learners don’t feel lost.
⚖️ Ethical Rules Every Beginner Must Follow
Learning hacking without ethics is dangerous and illegal. Ethical hacking is strictly based on permission, laws, and responsibility. As a beginner, you must always follow these rules:
✅ Test only on:
Your own systems
Legal practice labs
Authorized programs (like bug bounty platforms)
❌ Never:
Hack random websites
Steal data
Bypass security without permission
Perform attacks for fun or revenge
Breaking these rules can lead to serious legal trouble, even for beginners.
👉 This is why professional courses always include a dedicated ethics & legal awareness module before real practice.
🚀 How Tools + Ethics Shape Your Cybersecurity Career
When you combine:
✅ The right tools
✅ With the right ethics
You become a true ethical hacker, not a criminal.
With proper tool knowledge and ethical practice, you can move into:
Bug Bounty Hunting
Web Penetration Testing
SOC & Blue Team roles
Cybersecurity Analysis
Security Research
Ethics protect your career, freedom, and reputation in the cybersecurity world.
👉 This is why every serious beginner eventually upgrades to a complete ethical hacking course that teaches tools, labs, and legal safety together.
✅ With this, your entire “Basics of Hacking” learning roadmap content is now COMPLETE and professionally structured.